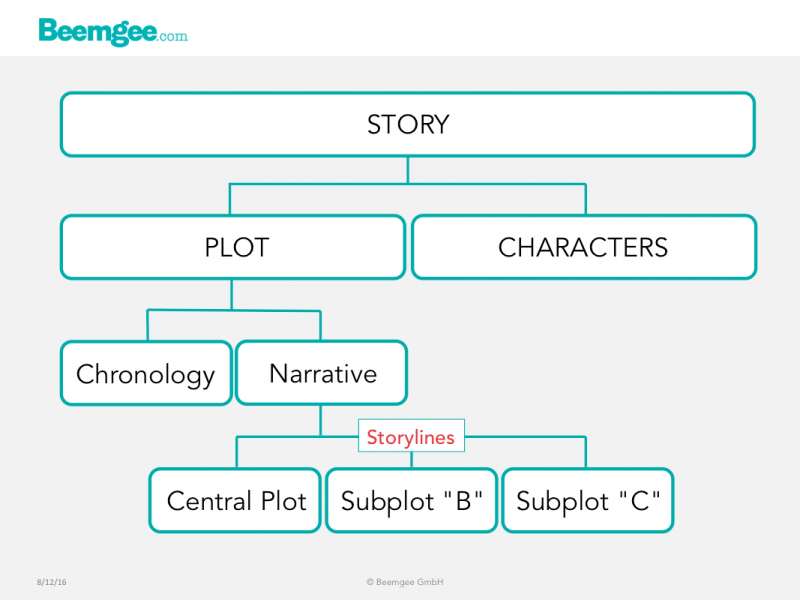
A plot arises out of the actions and interactions of the characters.
On the whole, you need at least two characters to create a plot. Add even more characters to the mix, and you’ll have possibilities for more than one plot.
Most stories consist of more than one plot. Each such plot is a self-contained storyline.
The Central Plot
Often there is a central plot and at least one subplot. The central plot is usually the one that arcs across the entire narrative, from the onset of the external problem (the “inciting incident” for one character) to its resolution. This is the plot that is at the(more…)
The term motif refers to any recurring element – in storytelling as in music or other arts.
Examples of elements that turn up repeatedly within a whole are an image on a tapestry or a particular sequence of notes in a symphony. The dispersal of these elements creates a pattern. It is therefore part of the artist’s craft to have some sort of design principle determine this pattern.
What motifs do
Motifs do not make a plot. But since they make patterns they are part of the structure of a story. And they help add a layer of meaning.
In other words, if a motif is present excessively in the first half of a story, and hardly at all in the second, then the author had better be aware of a reason for this uneven distribution. The distribution – the pattern – carries meaning to the audience. Remember, the audience yearns for meaning, is always striving to understand what the story is trying to convey at any given point. This demand for some sort of raison d’être for each element of a story, or for a sense of order within the whole, may well be unconscious to the audience much of the time, but ultimately the experience of the story is more satisfying when the audience can work out reasons and meaning.
In stories, motifs can be almost anything. Objects, actions, metaphors, symbols, colours, or images can be motifs. What defines an element as a motif is the systematic deployment within the story rather than the thing itself.
How motifs work
Motifs work best when(more…)
Theme is a binding agent. It makes everything in a story stick together.
To state its theme is one way of describing what a story is about. To start finding a story’s theme, see if there is a more or less generic concept that fits, like “reform”, “racism”, “good vs. evil”. The theme of Shakespeare’s Othello is jealousy.
Once this broadest sense of theme is established, you could get a little more specific.
Since a theme is usually (though not always) consciously posited by the author, it has some elements of a unique and personal vision of what is the best way to live. At best, this is expressed through the structure of the story, for instance by having the narrative culminate in a choice the protagonist has to make. The choices represent versions of what might be considered ways to live, or what is “right”.
But beware! This is a potential writer trap. See below.
How story expresses theme
Theme is expressed, essentially, through the audience’s reaction to how the characters grow. A consciously chosen theme seeks to convey a proposition that has the potential to be universally valid. Usually – and this is interesting in its evolutionary ramifications – the theme conveys a sense of the way a group or society can live together successfully.(more…)

